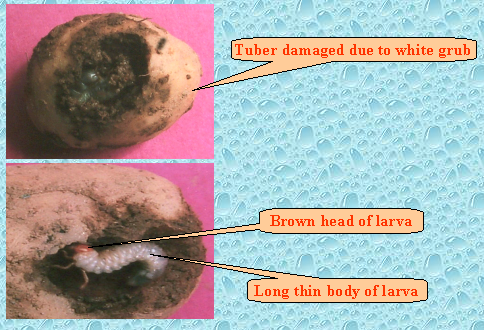
White Grub Management

Cultural and mechanical: In the endemic areas, autumn ploughing in hilly areas not only exposes the grubs to adverse conditions (low temperatures) but the exposed grubs also become prey of the birds. The use of nitrogenous fertilizers, especially ammonia and urea, at higher doses kill the first instar grubs. Besides, the light traps may also be used for collecting the beetles during night. The beetles can also be collected by shaking or jerking the host plants during night. The fallen beetles should be collected and destroyed by putting them either in kerosinized water or by burning. The host trees of adults (beetles) should be lopped or pruned and sprayed with contact insecticides before the emergence of beetles in June/July.
Chemical: Infestation
of white grubs can effectively be managed by applying insecticides to the soil
at earthing of potatoes when the grubs are young and delicate. Soil treatment
with granules of fensulfothion/quinalphos/phorate/ carbofuran or isofenphos @
2.0 units a.i/ha at earthing is recommended for the control of grubs. At the
time of beetle’s emergence, spraying of host trees with carbaryl,
fenitrothion,monocrotophos, endosulfan or quinalphos at 0.04% may register
effective control of beetles that are responsible for next generation grubs
damaging potatoes.
Biological: A number of bio-control agents are known to manage white grubs in different parts of the country. These should be encouraged either by conserving the existing populations or by introducing and establishing the known bio-control agents obtained from new localities. Some of the potential bio-control agents are: scoliids, Campsomeris collaris F., Scolia aureipennis Lepeletier and S. pustulata Magr.,pathogen like Bacillus popillae Dutky, Metarrhizium anisopliae (Metch.), Beauveria brongniartii (Sacc.) Petch, Isyr.and B. tenella (Del.), and entomophilic nematode, Steinernema sp.
Integrated management: The IPM schedule suggested for the management of cutworms has also been found beneficial for the management of white grubs in potatoes. Besides, other practices viz., removal of alternate/collateral hosts of the beetles from the vicinity and within potato crop, spraying of the beetle hosts and bunds with contact insecticides and early harvesting of potatoes in areas prone to white grubs.