

Mites (Acarina : Tetranychidae) BACK
Species complex
1. Two- spotted spider mite- Tetranychus urticae Koch.
2. Broad mite- Polyphagotarsonemus latus Banks
Tetranychus urticae Polyphagotarsonemus latus
Distribution:
Distributed widely throughout India. Damage due to broad mite is serious in Maharashtra and Karnataka during Kharif season and western UP and Punjab on early-planted Rabi potatoes. Besides, mite damage on potato crop has been observed around Gwalior (MP) and in Kangra valley (HP).
Host Range: Polyphagous.
Nature of damage and symptoms:
· Plants covered with dense webs harbouring sometimes thousands of mites.
·
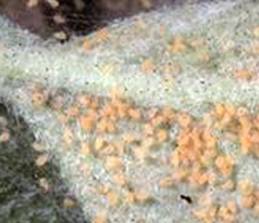 Suck
the cell sap from leaves and young plant tissues.
Suck
the cell sap from leaves and young plant tissues.
· Bronzing and curling of leaves and discoloration of leaves.
· Webbing of leaves, sepals and petals occur in case of two- spotted spider mite which give untidy look to the plant.
· The infestation is more severe under poly house conditions.
·
 In
case of severe infestation, the leaves are short and leathery. The pest is
responsible for 80-100% foliage infestation, causing 12 to 60% yield losses.
High humidity and moderate temperatures are quite conducive for the
multiplication of this mite and consequent damage.
In
case of severe infestation, the leaves are short and leathery. The pest is
responsible for 80-100% foliage infestation, causing 12 to 60% yield losses.
High humidity and moderate temperatures are quite conducive for the
multiplication of this mite and consequent damage.
Two-spotted spider mite colony with webbing Eggs of T. urticae mite
Identification:
· The cephalothorax and abdomen are fused. Therefore, the two different regions of the body are no longer distinguishable (Fig. 8).
· Generally, six pairs of appendages are attached to the cephalothorax: a pair of chelicerae, a pair of pedipalps and four pairs of legs.
·
 Eggs
are spherical, shiny white and translucent.
Eggs
are spherical, shiny white and translucent.
· Newly emerged larva (nymph) is dirty white in colour and possesses three pairs of legs.
· Protonymphs possess four pairs of legs and is slightly green/ yellow in colour.
· The male deutonymph is smaller than the female.
· Adults are bigger than deutonymphs with shining yellow to red coloured oval bodies, with a pair of chelicerae, pedipalps and eight legs on the cephalothorax region of the body.
Nymph
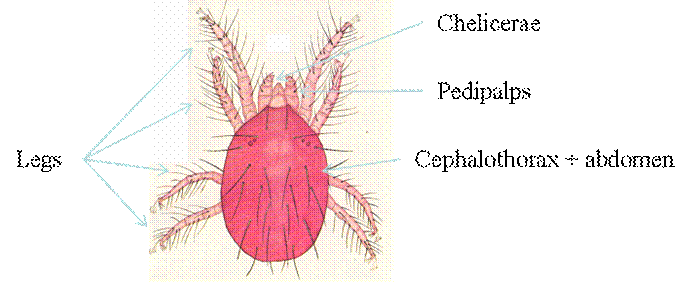
Figure: External morphology of adult mite
Life cycle:
· Eggs are laid singly on the underside of leaves often near the veins and depressions. Eggs hatch in about 2-4 days (Fig below).
· Larva becomes protonymphs in about 2 days. Protonymph after under going a quiescent stage develops into deutonymph. At this stage sexes are determined.
· Deutonymph stage lasts for 1-3 days and thereafter transform itself into quiescent pupal stage which stuck to the under side of leaves. The pupal stage lasts for about 2 days.
· Male longevity is 9-13 days and females live for 14-20 days.
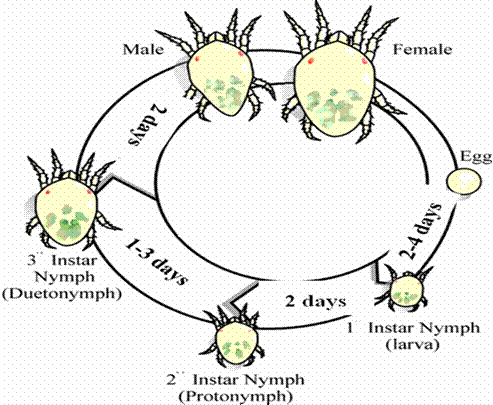
Figure : Life cycle of mites
· Under dry and hot conditions the multiplication of these mites is very high and the infestation is also severe.
Management:
· Destruction of severely affected plant parts mechanically during initial stage of infestation reduces mite population.
· Suitable crop rotations with non-host crops like wheat in pest prone areas and providing proper isolation to potato crop from susceptible hosts like chillies and brinjal.
· Delayed planting undertaken in last week of September for early crop and during middle of October for the main crop reduces the incidence and impact of the pest in Indo-Gangetic plains.
· Try to avoid dry conditions and spray frequently with plain water at least twice a week with sprinkler.
· Conservation of natural enemies such as Phytoseiid mites, Neioseiulus sp., efficient predatory mites and anthocorid bug, Orius sp. that regulates the pest under field conditions.
· Spray with Dicofol 18.5EC @ 2 ml or quinalphos 25EC @ 2ml/lit of water at a population level of 5-10 mites/plant.
· Application of Mancozeb (80WP) or micronized wettable sulphur (80WP) @ 2kg/ha respectively, is also effective. If the incidence of mite persists then repeat the spray application at 7-10 days.


Neioseiulus longispinosus Phytoseiid mite, Source: IIVR, Varanasi